NOAA APT Satellite Enhancements
The enhancement descriptions on this page come from the WXtoIMG manual (pages 2-5) and is (C) Copyright Central North Publishing Ltd.
- MSA
-
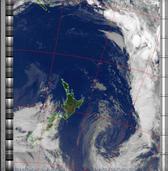 Example
ExampleMultispectral analysis. Uses a NOAA channel 2-4 image and determines which regions are most likely to be cloud, land, or sea based on an analysis of the two images. Produces a vivid false-coloured image as a result. This enhancement takes up to three options separated from the enhancement name by colons. The first option is the sea to land adjustment. The default value is 50 with the valid range being 0 to 100. This should be decreased if land appears blue, and increased if water appears green. The second option is the land to cloud adjustment. The default value is 50 with the valid range being 0 to 100. This should be decreased if cloud appears green and increased if land appears gray or white. The final option should be 0 to indicate warm or summertime analysis or 1 to indicate there are large cold regions. Note that perfect colouring is difficult to obtain, especially with low illumination angles. This enhancement does not use a palette nor is it temperature normalised.
- HVCT
-
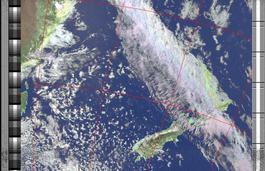 Example
ExampleSimilar to HVC (below), but with blue water and with colours more indicative of land temperatures.
- MCIR
-
 Example
ExampleColours the NOAA sensor 4 IR image using a map to colour the sea blue and land green. High clouds appear white, lower clouds gray or land/sea coloured, clouds generally appear lighter, but distinguishing between land/sea and low cloud may be difficult. Darker colours indicate warmer regions.
- ZA
-
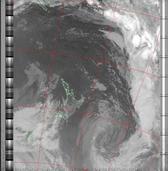 Example
ExampleNOAA general purpose meteorological IR enhancement option. Increases contrast by saturating the very low and very high temperature regions where there is typically very little information. This enhancement option is temperature normalised
- MSA-precip
- Same as MSA multispectral analysis, but high cold cloud tops are coloured the same as the NO enhancement to give an approximate indication of the probability and intensity of precipitation
- HVCT-precip
- Same as HVCT multispectral analysis, but high cold cloud tops are coloured the same as the NO enhancement to give an approximate indication of the probability and intensity of precipitation
- HVC-precip
- Same as HVC multispectral analysis, but high cold cloud tops are coloured the same as the NO enhancement to give an approximate indication of the probability and intensity of precipitation.
- sea
-
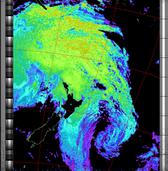 Example
ExampleCreates a false colour image from NOAA APT images based on sea surface temperature. Uses the sea surface temperature derived from just the sensor 4 image to colour the image. Land appears black and cold high cloud will also appear black. The sea surface temperature may be incorrect due to the presence of low cloud, or of thin or small clouds in the pixel evaluated, or from noise in the signal.
- therm
-
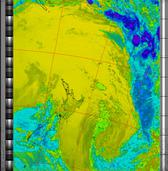 Example
ExampleProduces a false colour image from NOAA APT images based on temperature. Provides a good way of visualising cloud temperatures.
- NO
-
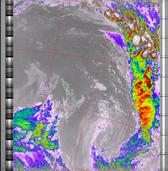 Example
ExampleNOAA colour IR contrast enhancement option. Greatly increases contrast in the darker land/sea regions and colours the cold cloud tops. Allows fine detail in land and sea to be seen and provides a very readable indication of cloud top temperatures. This enhancement option is temperature normalised.
- HVC
-
 Example
ExampleCreates a false colour image from NOAA APT images based on temperature using the HVC colour model. Uses the temperature derived from the sensor 4 image to select the hue and the brightness from the histogram equalised other image to select the value and chroma. The HVC colour model attempts to ensure that different colours at the same value will appear to the eye to be the same brightness and the spacing between colours representing each degree will appear to the eye to be similar. Bright areas are completely unsaturated in this model.
- unenhanced (pristine)
-
 Example
ExampleBest representation of the original digital data. Typically used to output images for further processing by other software. Pristine images are unenhanced, but unlike raw images have been normalised to produce images which represent, as best as the software is able to, the original digital data. No attempt is made to temperature normalise IR images. Disables gamma, sharpening, rotation and other enhancements.
- spectrogram
-
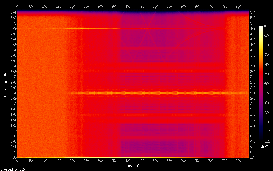 Example
ExampleA visual representation of the spectrum of frequencies in the satellite signal. Generated by the Sound eXchange software.
- recorded broadcast
-
Example (signal starts at 2 minutes, signal clear by 6 minutes)
This is a recording of the signal broadcast by the satellite in audio form. This is what all of the above images are generated from. These are rarely kept due to their large size (10-15MB per satellite pass, as much as 200MB per day). You'll likely only find a few in mid-february 2017 from when the processing system was being tested.